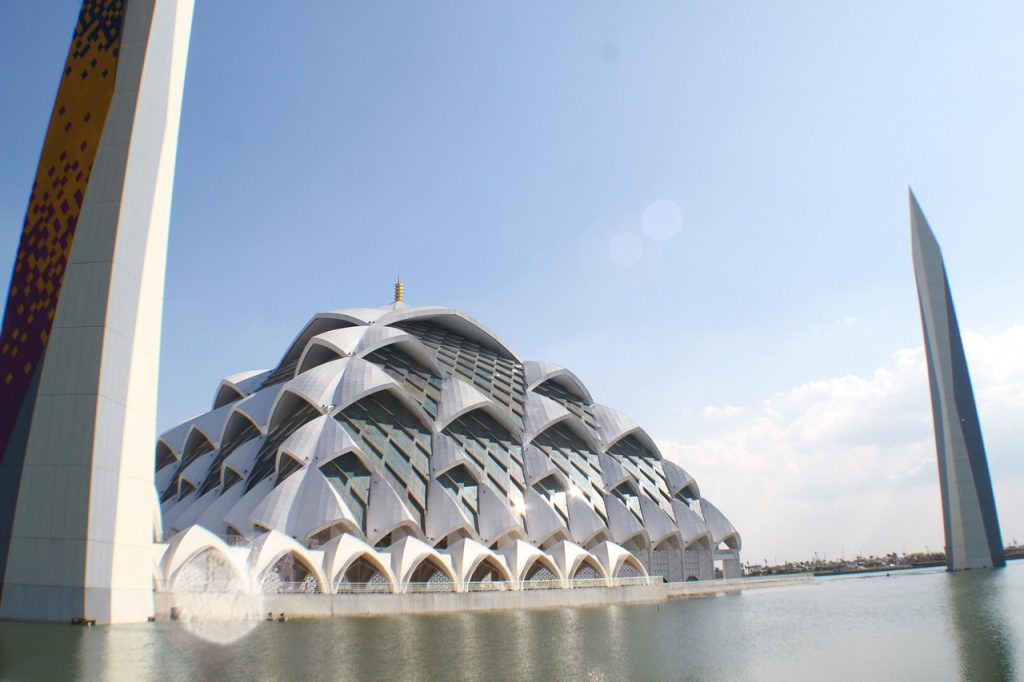
Buildings are more than just structures of concrete, steel, and glass; they are reflections of human needs, culture, and creativity. Every building, whether a home, hospital, school, or skyscraper, is designed with a specific purpose in mind, balancing functionality, safety, and aesthetic appeal.
Understanding the different types of buildings, their unique designs, and how architecture responds to their intended use offers valuable insights into both the art and science of construction. In this guide, we will explore ten major building types, highlighting their architectural features, primary functions, and the design principles that make them effective and enduring spaces.
10 Types of Buildings: Architecture, Function, and Design

This article explores 10 major types of buildings, examining their architectural characteristics, primary functions, and key design considerations. Each building type is shaped by its purpose, users, location, and environmental conditions, resulting in distinct design approaches and construction requirements.
1. Residential Buildings
Residential buildings are designed for people to live in. Their primary purpose is to provide safe, comfortable, and private spaces for individuals and families.
Common Types
Residential buildings include single-family houses, apartments, condominiums, townhouses, and villas. They can range from modest homes to luxury residences.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Design priorities focus on comfort, privacy, natural lighting, ventilation, and efficient use of space. Residential architecture often reflects cultural traditions and lifestyle preferences. Modern residential design emphasizes energy efficiency, sustainability, flexible layouts, and integration of indoor and outdoor living spaces.
Also read: Construction Apprenticeships: A Complete Guide for Beginners
2. Commercial Buildings
Commercial buildings are used for business activities such as retail, offices, banking, hospitality, and entertainment.
Common Types
These include office buildings, shopping malls, retail stores, hotels, restaurants, and mixed-use commercial complexes.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Commercial architecture prioritizes accessibility, visibility, functionality, and customer experience. Design elements often focus on branding, circulation flow, safety, and compliance with building codes. Modern commercial buildings increasingly incorporate open-plan layouts, smart technologies, and sustainable materials to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.

3. Industrial Buildings
Industrial buildings support manufacturing, processing, storage, and distribution of goods.
Common Types
Factories, warehouses, power plants, workshops, and logistics centers fall into this category.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Industrial architecture emphasizes durability, efficiency, and adaptability. Large open spaces, high ceilings, strong structural systems, and robust flooring are common features. Design must accommodate heavy machinery, material handling systems, and safety regulations. Ventilation, fire protection, and energy efficiency are also critical considerations.
4. Institutional Buildings
Institutional buildings serve public or community needs, often providing essential services.
Common Types
Schools, universities, hospitals, libraries, government offices, and courthouses are examples of institutional buildings.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Design focuses on accessibility, safety, and functionality for diverse users. Educational buildings emphasize learning environments, natural light, and acoustics. Healthcare buildings require specialized layouts for patient care, hygiene, and efficient movement of staff and equipment. Institutional architecture often conveys stability, trust, and public identity.
5. Educational Buildings
Educational buildings are dedicated specifically to teaching, learning, and academic research.
Common Types
Primary schools, secondary schools, colleges, universities, training centers, and research facilities.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Design supports learning by creating flexible classrooms, collaborative spaces, and quiet study areas. Good lighting, acoustics, and ventilation are essential. Modern educational buildings increasingly incorporate technology-enabled spaces, adaptable layouts, and outdoor learning areas to support evolving teaching methods.
6. Healthcare Buildings
Healthcare buildings provide medical services, treatment, recovery, and wellness support.
Common Types
Hospitals, clinics, medical centers, rehabilitation facilities, and specialized treatment centers.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Healthcare architecture prioritizes patient safety, hygiene, efficiency, and comfort. Clear circulation paths, infection control measures, and privacy are critical. Design often includes calming colors, natural light, and access to green spaces to promote healing. Technological integration and emergency preparedness are also key factors.
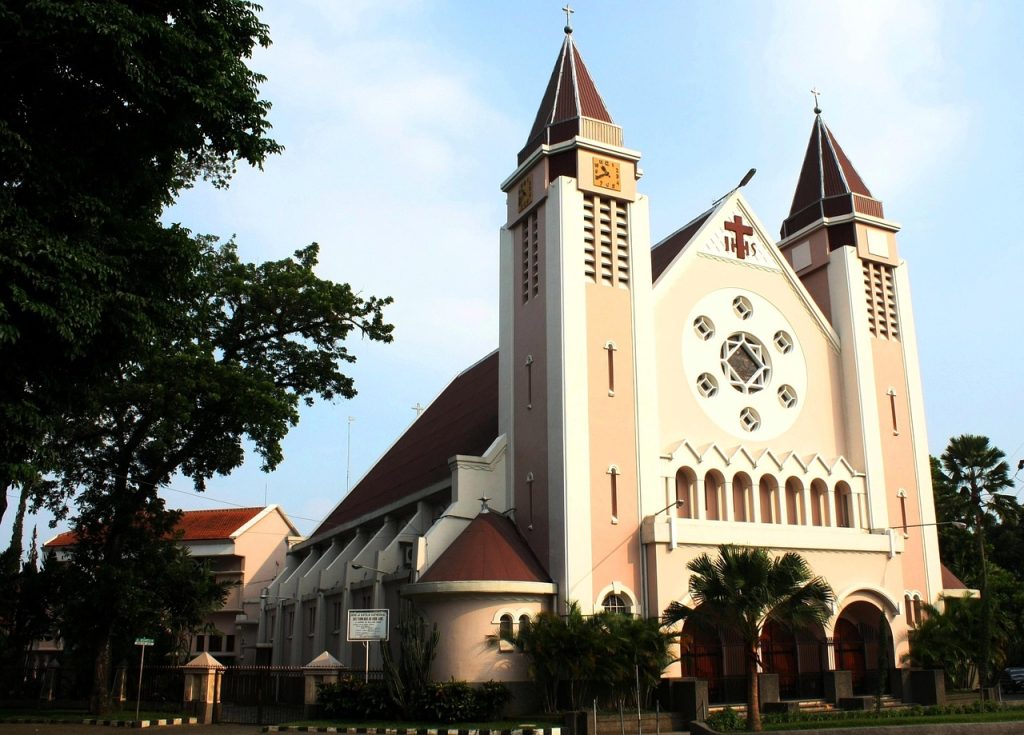
7. Religious Buildings
Religious buildings provide spaces for worship, spiritual practices, and community gatherings.
Common Types
Churches, mosques, temples, synagogues, monasteries, and shrines.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Religious architecture often reflects cultural traditions, beliefs, and symbolism. Design emphasizes spiritual atmosphere, sacred geometry, and ceremonial spaces. Materials, lighting, and ornamentation are carefully chosen to enhance reverence and contemplation. Many religious buildings also serve as cultural landmarks and community centers.
8. Cultural and Recreational Buildings
These buildings support cultural expression, leisure, and social interaction.
Common Types
Museums, theaters, galleries, concert halls, sports arenas, stadiums, and community centers.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Design focuses on user experience, acoustics, visibility, circulation, and safety. Cultural buildings often feature iconic architectural forms that represent creativity and identity. Recreational buildings require durable materials, crowd management strategies, and flexible spaces for diverse events and activities.
9. Transportation Buildings
Transportation buildings facilitate the movement of people and goods.
Common Types
Airports, train stations, bus terminals, seaports, and transit hubs.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Efficiency, wayfinding, and safety are top priorities. Design must manage large volumes of users while ensuring smooth circulation and security. Transportation architecture often combines functionality with symbolic elements that reflect the city or region it serves. Sustainability and integration with public transport systems are increasingly important.
10. Mixed-Use Buildings
Mixed-use buildings combine multiple functions within a single structure or development.
Common Types
Developments that include residential, commercial, office, and recreational spaces in one integrated environment.
Architectural and Design Considerations
Design focuses on zoning, circulation separation, and compatibility between different uses. Mixed-use buildings maximize land efficiency and promote walkable communities. They often include shared amenities, public spaces, and sustainable design strategies to support urban density and reduce transportation needs.
Key Architectural Principles Across Building Types
While each building type has unique requirements, several architectural principles apply universally:
Functionality
The building must effectively serve its intended purpose, supporting the activities of its users.
Safety and Compliance
All buildings must meet structural, fire, accessibility, and safety standards.
Sustainability
Modern architecture emphasizes energy efficiency, responsible material use, and environmental impact reduction.
Aesthetics
Visual appeal contributes to user satisfaction and cultural identity.
Also read: Sustainability in Construction: Building a Greener Future
Adaptability
Flexible design allows buildings to evolve with changing needs over time.
The Role of Design in Shaping Human Experience
Architecture is not just about constructing structures; it shapes how people feel and behave within spaces. Well-designed buildings enhance productivity, learning, healing, and social interaction. Poor design, on the other hand, can lead to discomfort, inefficiency, and long-term operational challenges.
As urbanization increases and populations grow, thoughtful building design becomes essential for sustainable development. Architects and planners must balance aesthetics, function, cost, and environmental responsibility to create buildings that serve both present and future generations.
Future Trends in Building Design
The future of building design is shaped by innovation and global challenges. Smart buildings equipped with digital systems improve efficiency and user comfort. Sustainable architecture reduces carbon footprints through renewable energy, green roofs, and passive design strategies. Modular and prefabricated construction methods increase speed and quality while reducing waste.
Human-centered design is also gaining importance, focusing on wellness, inclusivity, and emotional connection to space. Buildings are increasingly seen as living systems that interact with people and the environment.
Conclusion
Understanding the 10 main types of buildings provides valuable insight into how architecture responds to human needs and societal development. Each building type from residential homes and educational institutions to healthcare facilities and transportation hubs serves a distinct function that influences its design, structure, and materials.
Architecture is a powerful tool that shapes daily life, cultural identity, and economic activity. By appreciating the relationship between function, design, and architecture, readers gain a deeper understanding of the built environment and the thoughtful planning required to create spaces that are safe, efficient, inspiring, and sustainable.
As the world continues to evolve, well-designed buildings will remain essential to supporting communities, fostering innovation, and improving quality of life for people everywhere.
Gracia Rena
Gracia is a co-owner of the company and a seasoned professional with over 20 years of experience in the hospitality industry. Her impressive background includes roles at major organizations such as Marriott, Accor, Banyan Tree, Sudamala, and Singapore Airlines.
With a profound understanding of luxury service standards and operational excellence, Gracia brings invaluable expertise to the business. Her strategic insight and dedication to quality have been instrumental in shaping the company’s growth, ensuring its continued reputation for delivering exceptional value and innovation in hospitality and commercial projects across the region.





